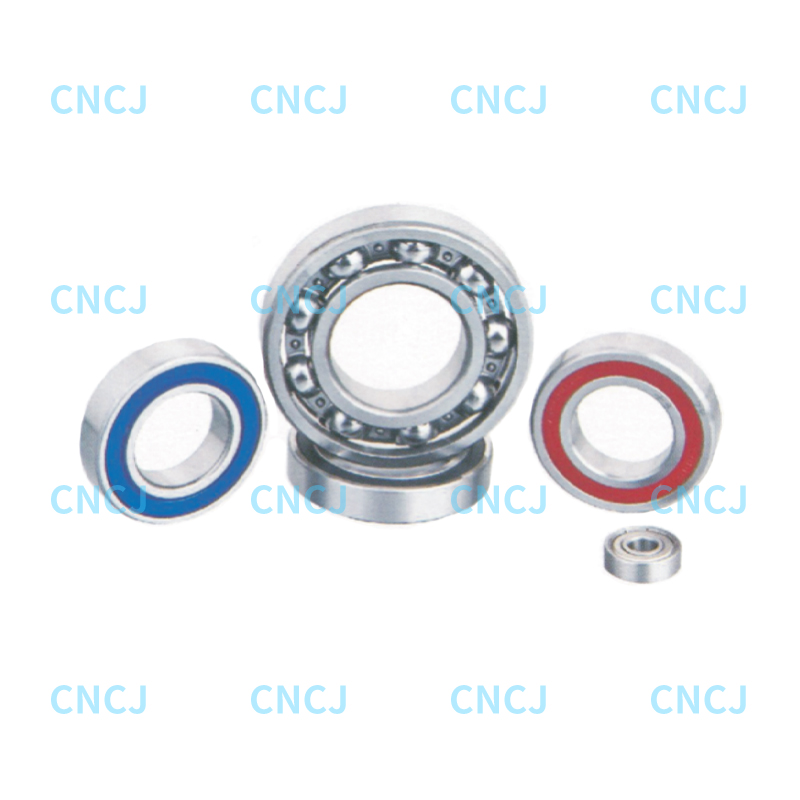
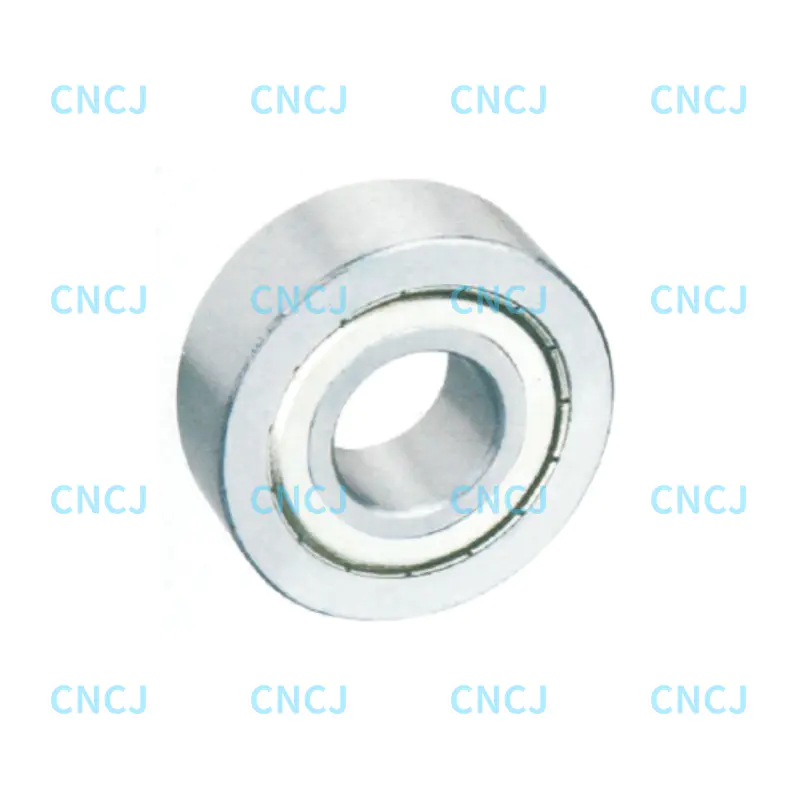
Deep groove ball bearings are the most common type of rolling bearings. They have a simple structure and a wide range of uses. They have the following core features:
Structural design: It consists of inner and outer ring steel balls and a cage. The inner and outer rings have deep groove raceways and can withstand radial and axial bidirectional loads.
Performance advantages: small friction coefficient (0.0010~0.0015) high speed (limit speed can reach more than 20000rpm) low manufacturing cost.
Application scenarios: From household appliances (such as washing machine motors) to industrial equipment (motor gearboxes and automobile wheels), covering more than 80% of bearing usage needs.
2. Six precautions in use
Installation specifications
Cold installation method: Use a special sleeve to evenly knock the inner ring of the bearing (do not knock the outer ring directly). It is recommended to heat the interference fit to 80~120℃ for hot installation.
Alignment requirements: The eccentricity between the shaft and the bearing seat must be less than 0.05mm, otherwise it will cause early fatigue peeling.
Lubrication management
Grease selection: low viscosity grease (such as Mobil Polyrex EM) for high speed, and composite calcium sulfonate grease for high temperature conditions.
Replenishment cycle: For every 15℃ increase in operating temperature, the lubrication cycle is shortened by half (for example, grease needs to be replenished every 2000 hours at 70℃).
Load control
Radial load: must not exceed the basic rated dynamic load Cr (such as 6208 bearing Cr=29.1kN).
Axial load: must not exceed 20% of the radial load, otherwise angular contact bearings need to be used instead.
Operation monitoring
Abnormal vibration: when the acceleration value is greater than 10m/s², the machine needs to be stopped for inspection.
Temperature rise warning: the ambient temperature of +40℃ is the normal threshold, and lubrication or alignment problems need to be checked if it exceeds.
Disassembly points
Special tools: when using a puller for disassembly, the inner and outer rings need to be tightened synchronously to avoid deformation of the cage.
Scrap standard: Replacement is required when pitting (diameter > 1mm) or clearance increases to 3 times the initial value.
Storage conditions
Rust prevention measures: Relative humidity < 65%, 3 years shelf life for sealed packaging.
Stacking requirements: Store flat, no more than 5 layers, to avoid deformation of the outer ring.
3. Typical faults and solutions
|
Fault phenomenon
|
Possible cause
|
Solution
|
|
Abnormal noise
|
Insufficient lubrication/contamination
|
Replace grease after cleaning
|
|
Temperature rise too fast
|
Too small clearance/overload
|
Adjust clearance or reduce load
|
|
Inner and outer ring cracks
|
Stress concentration during installation
|
Reinstall using hydraulic method
|

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español