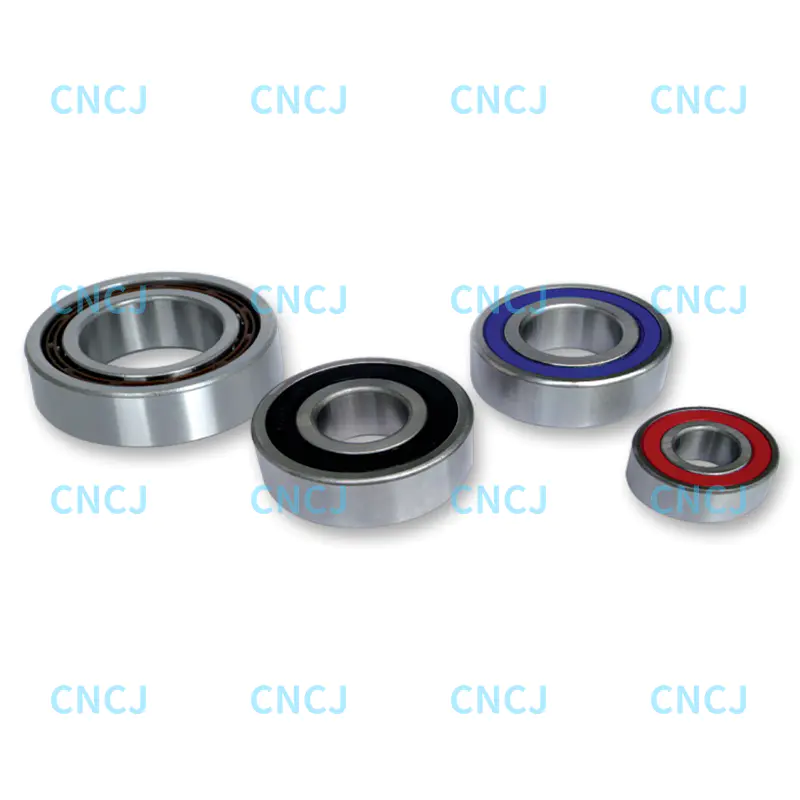
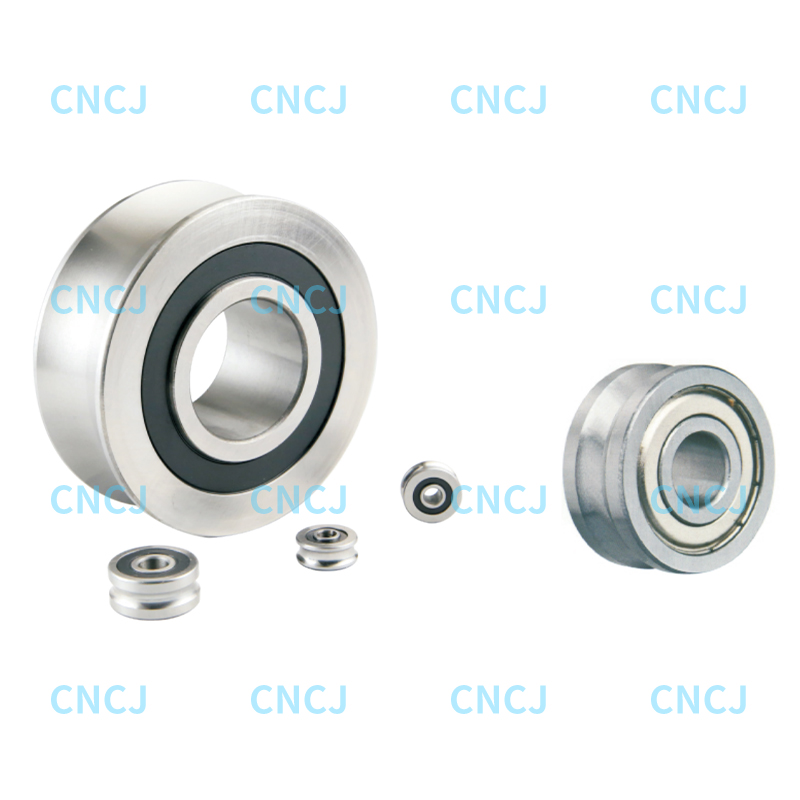
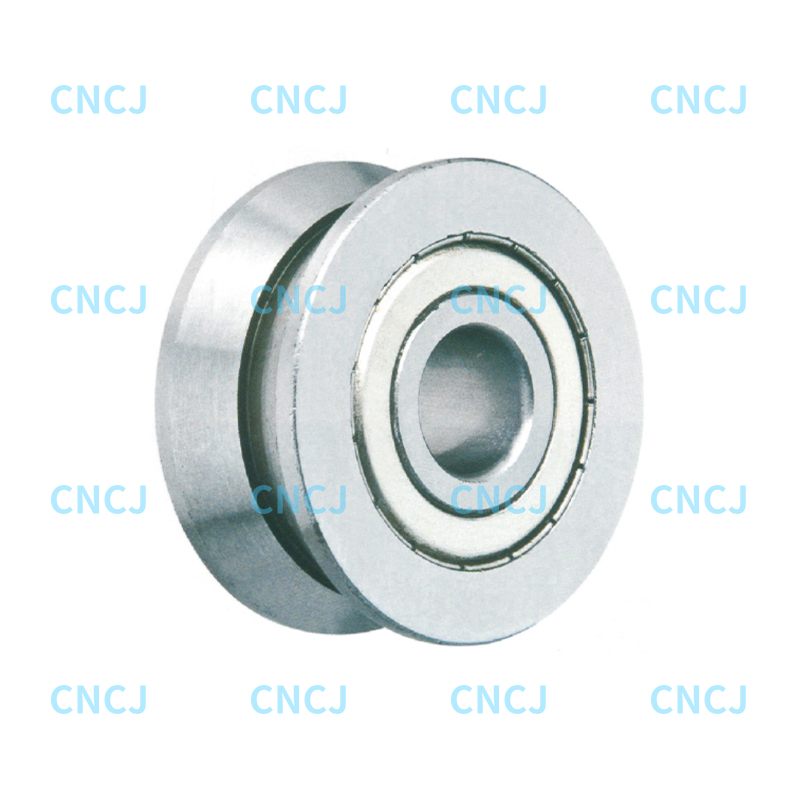
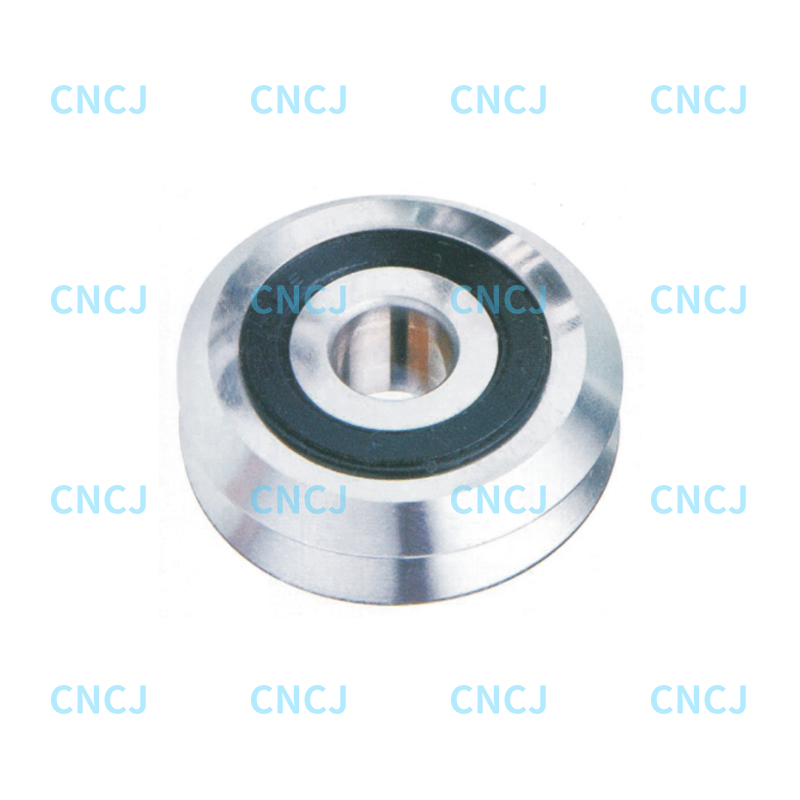
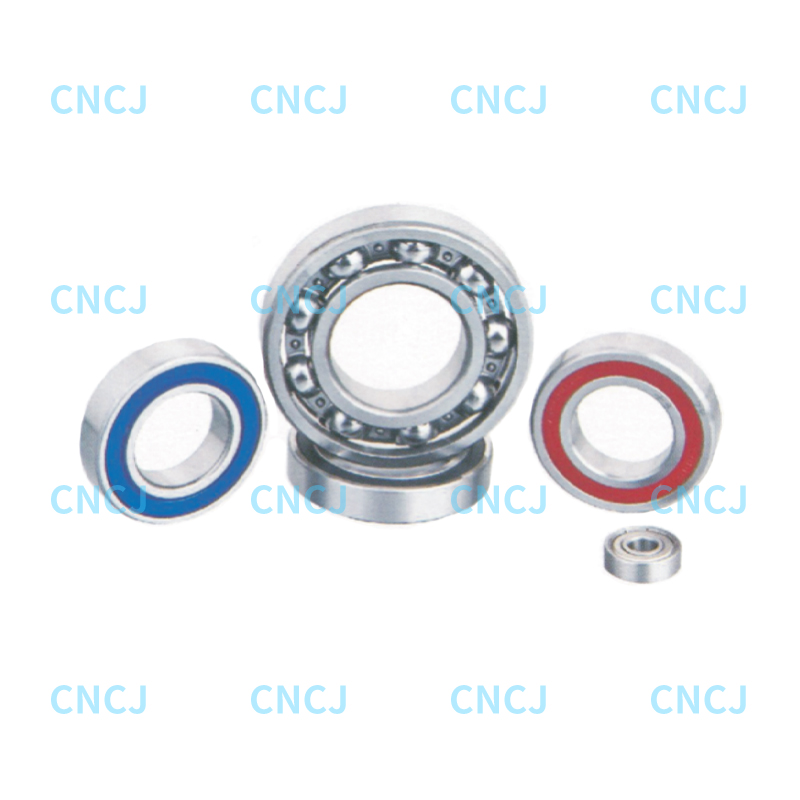
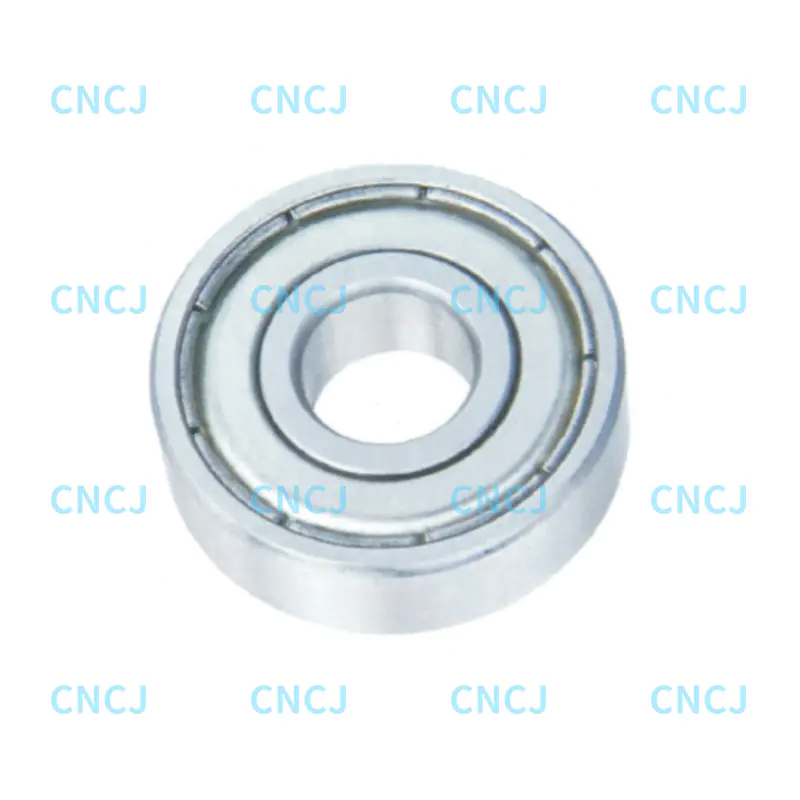
In industrial machinery, automated production lines, and heavy equipment, track roller bearings play a crucial role. They support and guide the movement of rolling components, ensuring efficient operation of the equipment.
However, with the wide variety of bearing models and performance characteristics on the market, many engineers and purchasing personnel are often confused: "How to choose the right track roller bearing?" This article will analyze the working principle, key parameters, material selection, application scenarios, and maintenance suggestions to help you make a reasonable choice.
1. Working Principle of Track Roller Bearings
A track roller bearing is a type of bearing that can roll or slide on a track. The core principle is:
Rolling Load Bearing
The rollers roll on the track, distributing radial and axial loads to the raceway and bearing structure, reducing friction and improving operating efficiency.
Precise Guidance
The rollers maintain a stable trajectory as they move along the track, ensuring the precision and smoothness of the mechanical structure.
Adaptability to High Loads and Long Strokes
Track roller bearings can withstand large loads and are suitable for long-distance sliding or repetitive motion scenarios.
Understanding the working principle helps in determining whether the bearing meets the equipment's operating conditions during selection.
2. Key Parameters for Selecting Track Roller Bearings
The following main parameters need to be considered during selection:
Load Capacity
Select the bearing specifications based on the maximum load capacity of the equipment, including radial and axial loads, to ensure long-term stable operation of the bearing.
Rolling Speed
High-speed operation scenarios require low-friction, high-precision roller bearings to reduce heat generation and wear.
Size Specifications
Determine the model based on the track width, roller diameter, and bearing spacing to ensure proper installation space.
Accuracy Level
Precision equipment requires high-precision roller bearings to ensure smooth movement and reduce vibration and noise.
Life and Durability
Refer to the rated life and number of cycles provided by the manufacturer, and evaluate the replacement cycle based on actual usage frequency.

3. Material Selection
The material directly affects the wear resistance, load capacity, and service life of the bearing. Common materials include:
Bearing Steel (GCr15 or 52100)
Strong wear resistance, suitable for industrial machinery and high-load environments. Stainless Steel
Offers excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for humid or chemical environments.
Polyurethane or Nylon Rollers
Lightweight and offer good vibration damping, suitable for light-duty equipment and low-noise applications.
The choice of different materials should be based on a comprehensive consideration of load, speed, environmental humidity, and corrosion requirements.
4. Application Scenarios
Track roller bearings are suitable for a variety of industrial and mechanical applications, including:
Automated Production Lines
Used in conveyor systems, robotic arms, and robot guide rails to improve equipment accuracy and stability.
Heavy Machinery
Carries heavy loads in cranes, machine tool slides, or assembly lines, ensuring smooth movement.
Logistics and Warehousing Equipment
Slide rails, conveyor chains, and handling systems rely on roller bearings to reduce friction and improve transportation efficiency.
Precision Equipment
Such as measuring instruments or automated testing equipment, requiring high precision and low-noise rolling.
5. Maintenance and Usage Recommendations
Regular Lubrication
Choose a suitable lubricant based on the bearing material and load conditions. Regular oiling or greasing can extend the lifespan.
Cleaning and Dust Prevention
In dusty or contaminated environments, take precautions to prevent particles from entering the raceway and causing wear.
Proper Installation
Ensure that the rollers are parallel to the track and the roller spacing is uniform to prevent uneven loading and abnormal noise.
Monitor Wear
Regularly check the roller surface and track for wear, and replace aging or damaged bearings promptly.
Choosing the right track roller bearing requires comprehensive consideration of load capacity, rolling speed, dimensions, precision grade, and material characteristics. Combining this with specific application scenarios and routine maintenance can significantly improve the stability, accuracy, and lifespan of mechanical equipment. Scientific selection not only ensures efficient operation but also reduces maintenance costs, providing reliable support for industrial production and automation systems.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español